On This Page: [hide]
The undoubtful surge in VPN adoption has attracted the attention of governments worldwide, prompting diverse regulatory responses. As a result, many internet users are looking for ways to bypass VPN blocks.
In many parts of the world, there are rules and limitations in place against using Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). But the big question is: Can a government really stop VPNs? And can they set up strong barriers to prevent all kinds of VPN connections?
This article aims to shed light on the various laws and regulations related to VPNs and how governments attempt to control their use across different countries (the so-called geo-restrictions). Further, we will dissect the sensitive relationship between governments and VPNs, exploring their significance, detection mechanisms, implications, legal considerations, and the evolving landscape of VPN technology.
Let’s dive in!

Is It Possible for a Government to Block VPN Services?
Absolutely, a government does have the ability to block VPN services.
They can take steps like shutting down specific VPN ports and blocking well-known VPN provider websites. Moreover, they can create a list of IP addresses to prevent access, and in more advanced cases, they might use a technique called VPN deep packet inspection (DPI) to keep an eye on VPN activities.
The global landscape concerning VPNs varies widely, reflecting governments’ diverse perspectives on online privacy, national security, and information control. While some nations actively promote VPN usage for legitimate purposes, others have imposed stringent regulations or outright bans. For instance, countries like Canada and Germany recognize the value of VPNs for enhancing cybersecurity, while nations like China, Russia, and Iran have employed strict measures to control VPN availability and usage.
Let’s take a deeper look at China, which has a strict policy of controlling what its citizens can access on the internet. In the past, China has effectively blocked certain VPN servers, making it quite challenging for people within the country to use VPNs for unrestricted internet access.
The story doesn’t end with China. Other countries like Iran, Russia, and Turkey have also taken measures to control VPN usage. This might involve imposing restrictions on VPN services or even completely banning specific VPN providers.
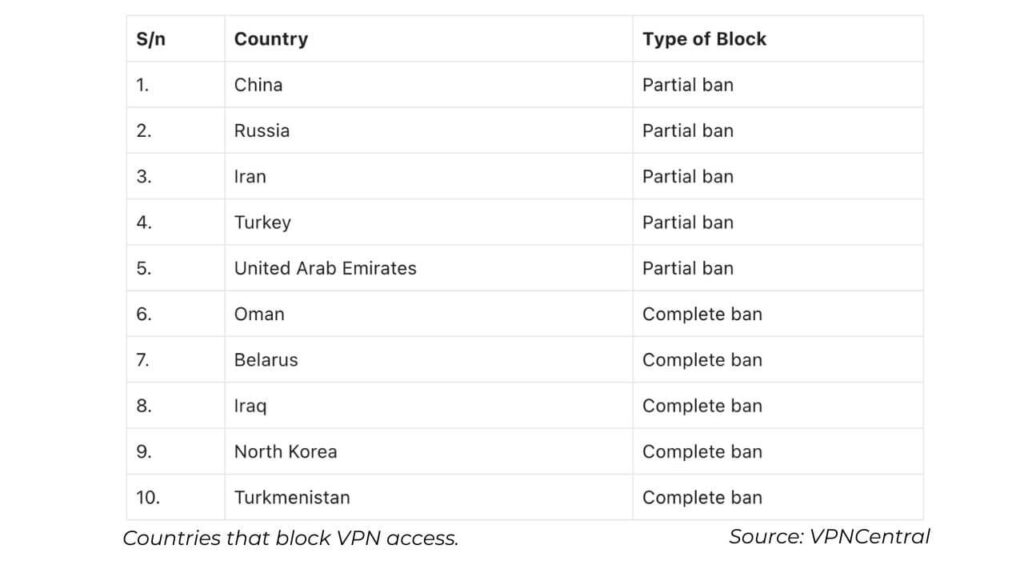
Countries that Block VPNs
Certain countries have implemented partial limitations or regulations on the utilization of VPNs, while in contrast, some countries completely obstruct access to VPN services.
Government and ISP Oversight
Both governmental entities and your Internet Service Provider (ISP) possess the capability to ascertain whether you are employing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or not. This discernment arises from their capacity to observe the trajectory of your internet traffic as it traverses through an encrypted server.
Regrettably, there exists no viable avenue to circumvent this phenomenon, as encryption constitutes a fundamental pillar of VPN functionality. Consequently, this intrinsic attribute illuminates the mechanism through which governments may potentially prosecute individuals for engaging with VPNs in jurisdictions where their usage is proscribed.
A Matter of Legal Context
The significance of this matter diminishes substantially if VPN usage is sanctioned within the legal framework of your nation of domicile. It is pivotal to acknowledge that, in a vast majority of instances, governmental bodies merely discern the presence of VPN usage; their purview does not extend to discerning the specifics of your online activities, internet history, or authentic IP address. This encapsulation is achieved through the comprehensive encryption employed by your VPN, thereby shielding this trove of data from prying eyes.
Governments’ decisions to regulate or ban VPNs stem from concerns over national security, content control, and circumvention of censorship. In China, the “Great Firewall” represents a formidable barrier to unfettered internet access, effectively curtailing citizens’ access to external information. Such restrictions impact citizens’ digital freedom, hamper business operations, and stifle innovation. The case of Russia serves as a reminder of the potential for VPN restrictions to facilitate increased surveillance and curtail online privacy.
How Do Governments and ISPs Block VPNs?
These are the most popular methods that both governments and ISP providers utilize to block access to VPN services worldwide.
Address Exclusion: Blacklisting VPN IPs
When individuals connect to a VPN, they receive an IP address from the VPN server, ensuring their anonymity.
Yet, two prevalent methods for IP address utilization are whitelisting and blacklisting. Whitelists encompass approved IP addresses that can pass through firewalls or routers, whereas blacklists encompass those barred from passage.
Hence, the blacklisting technique involves cross-referencing incoming IP addresses with a repository of recognized VPN IP addresses. It then denies access to addresses matching any on the blacklist. This approach proves especially potent when governments place entire server networks of major VPN providers on the blacklist.
Bandwidth Throttling: Manipulating Internet Speeds
Bandwidth throttling denotes the intentional slowing of internet speeds for specific traffic types by ISPs. This measure can hinder or render it impossible for users to connect to VPN services.
Governments can enact throttling by identifying traffic traits and impeding their flow. For instance, encrypted traffic routed through non-standard ports can be discerned and decelerated.
This impediment creates challenges for users striving to establish and employ VPN connections effectively.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Real-time Content Scrutiny
DPI represents a technique enabling governments to scrutinize the content of online traffic as it traverses the network.
In this process, designated checkpoints actively analyze data packets in transit across the network. Determined by governmental or ISP regulations, real-time judgments are executed based on packet content.
These actions encompass alerts, blocks, re-routing, or data logging, in alignment with the DPI findings.
Governments can exploit DPI to identify VPN traffic by identifying specific traffic attributes. For instance, VPN traffic often involves encryption and non-standard port routing. DPI scrutinizes the destination port numbers of data packets and compares them with a roster of recognized VPN port numbers.
For instance, OpenVPN predominantly employs UDP port 1194, while WireGuard commonly utilizes UDP port 51820. By detecting these attributes, governments can pinpoint VPN traffic and impede its flow.
Legal Constraints and Penal Ramifications
Certain nations have enacted legislation that prohibits the use of VPN services. These laws can be leveraged to prosecute or intimidate individuals endeavoring to utilize VPNs within the country.
For instance, in Oman, violating VPN usage mandates a fine exceeding $1,000. In specific scenarios, governments may target VPN providers themselves. They might enact laws rendering VPN operations illegal within the nation, or institute criminal penalties for VPN providers violating these mandates.
For example, China obstructs access to renowned VPN provider websites, thereby rendering signup and VPN acquisition unattainable. This approach effectively curtails VPN services within the country.
How to Circumvent VPN Blocks

Step 1: Choose a Reliable VPN Provider
Select a reputable VPN service that offers strong encryption, a wide range of server locations, and robust security features. This is crucial for maintaining your online privacy while bypassing VPN blocks.
Step 2: Configure VPN Settings
- Download and install the VPN application on your device.
- Launch the app and log in with your credentials.
- Choose a server location outside the restricted region. Opt for servers with a history of working well against blocks.
Step 3: Utilize Obfuscated Servers
Many VPN providers offer obfuscated servers designed to bypass VPN blocks. These servers disguise your VPN traffic as regular internet traffic, making it harder for ISPs to detect and block it.
Step 4: Change VPN Protocols
Switch to alternative VPN protocols like OpenVPN with TCP or Stealth VPN. These protocols often help you overcome deep packet inspection (DPI) used to identify VPN traffic.
Step 5: Try Different Ports
Some ISPs block specific ports commonly used by VPNs. Experiment with different ports (e.g., TCP port 443, which is used for HTTPS) to find one that works despite the restrictions.
Step 6: Use Split Tunneling (if available)
Split tunneling allows you to route only specific traffic through the VPN while letting other traffic use your regular internet connection. This can help you bypass blocks while maintaining optimal connection speeds for non-restricted content.
Step 7: Enable Stealth Mode (if available)
Stealth mode or “obfuscation” is a feature offered by some VPN providers. Enabling this mode disguises your VPN traffic as regular traffic, making it more challenging to block.
Step 8: Use DNS Over HTTPS (DoH)
Enable DNS over HTTPS in your browser or device settings. This secures your DNS queries and prevents ISPs from intercepting and manipulating your DNS traffic to block VPN connections.
Step 9: Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
Sometimes, blocks can be triggered by cached data. Clear your browser’s cache and cookies, then restart your browser after connecting to the VPN.
Step 10: Contact Customer Support
If you’re still experiencing VPN blocks, contact your VPN provider’s customer support. They might provide additional insights or server recommendations to help you bypass the restrictions.
Will VPNs Continue to Be Blocked in the Future?
Predicting the landscape of VPN blocks in the near future presents a complex challenge shaped by the ever-evolving interplay between technological advancements and regulatory measures. As governments and institutions continue to tighten their grip on digital control, it’s likely that VPN blocks will remain a focal point. We can anticipate a rise in more sophisticated blocking techniques, with increased emphasis on AI-powered detection of VPN traffic.
As privacy concerns heighten, VPN providers may intensify their efforts to innovate and create novel solutions to bypass these blocks. However, it’s also possible that governments will respond with countermeasures, potentially leading to a cat-and-mouse game between VPN developers and regulatory authorities. As the battle between open access and restricted control unfolds, the future of VPN blocks will likely be characterized by dynamic shifts and sophisticated strategies, ultimately influencing the accessibility and openness of the online realm.