On This Page: [hide]
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, where online privacy and security are paramount concerns, Virtual Private Network (VPN) protocols emerge as the guards of our online experiences.
These intricate sets of rules and encryption techniques form the backbone of VPN services, determining the level of protection, speed, and functionality online users can expect. As the demand for secure internet connections continues to surge, understanding the nuances of various VPN protocols becomes essential for anyone seeking to navigate the digital realm with confidence and peace of mind. It is also noteworthy, that as per statistics, around 35% of global internet users have embraced VPN services. This number reflects a noteworthy upsurge from earlier periods.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of VPN protocols, ultimately guiding you toward informed decisions in fortifying your online presence. So, let’s begin, question by question, until your thirst for knowledge is fulfilled!

What Is a VPN Protocol?
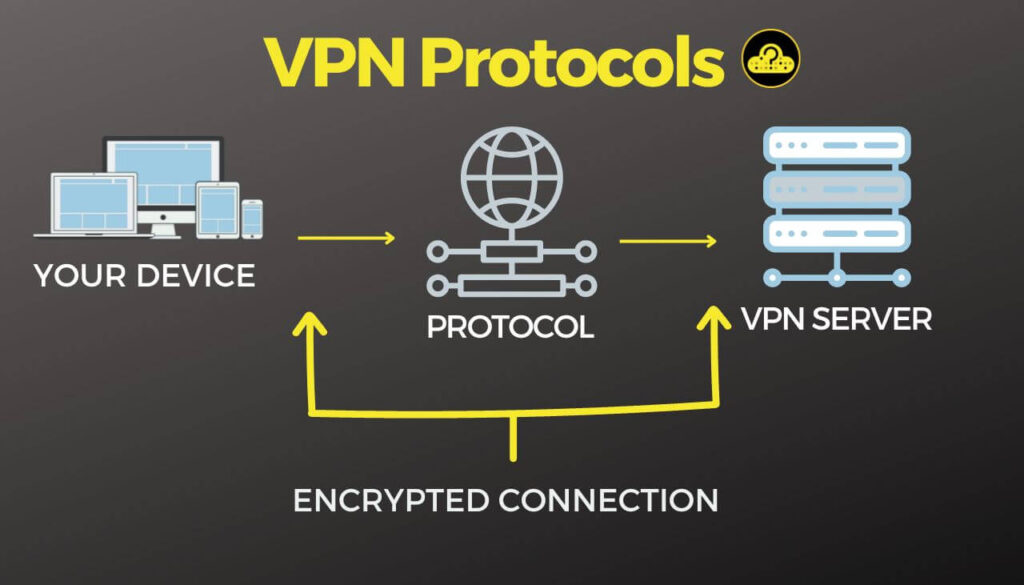
A VPN protocol refers to a standardized set of rules, procedures, and cryptographic algorithms that govern the way data packets are encapsulated, transmitted, and decrypted during their journey between a user’s device and a remote VPN server. These protocols are integral to the functioning of Virtual Private Networks and play a crucial role in establishing a secure, encrypted, and private communication channel over public networks like the internet.
The core objective of VPN protocols is the implementation of diverse encryption methods aimed at safeguarding data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity, thereby thwarting unauthorized access and potential cyber threats. Among the array of prevalent VPN protocols, notable examples include OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, IKEv2/IPsec, PPTP, and SSTP, each wielding distinct merits and limitations in domains like security, speed, and compatibility.
Consider you’re dispatching a delicate glass sculpture to an art gallery across the country. To ensure its safe arrival, you’d meticulously cushion it in protective foam, label the package as “fragile,” and choose a reputable shipping carrier. On the other hand, if you were sending a stack of sturdy books to a friend, the need for extra precautions and fragile labels would be unnecessary.
Much like the role of protective foam in shipping, various VPN protocols act as either robust shields or streamlined channels when transmitting data across a VPN. Opting for minimal encryption and authentication (similar to reducing foam padding) can expedite data transfer, but it also exposes online traffic to potential risks.
Consequently, depending on whether specific situations prioritize speed or security, utilizing distinct protocols that accentuate different facets of data exchange emerges as the most necessary choice. As we delve deeper into this article, we explore specific scenarios where certain protocols may excel.
Why Are VPN Protocols Important?
VPN protocols play a pivotal role in ensuring the efficacy, security, and versatility of Virtual Private Networks. These protocols dictate how data is encapsulated, transmitted, and decrypted as it travels between a user’s device and a remote VPN server. Their significance lies in several key aspects which can be grouped in the following ways:
- Security. VPN protocols employ advanced encryption techniques to secure data transmissions, safeguarding sensitive information from potential cyber threats, hackers, and unauthorized access. Strong encryption is crucial, especially when using public networks, as it prevents eavesdropping and data interception.
- Privacy. By anonymizing users’ IP addresses and routing their traffic through encrypted tunnels, VPN protocols enhance online privacy. This shields user activities from ISPs, government surveillance, and other entities that might seek to monitor or track online behavior.
- Data Integrity. VPN protocols ensure that data remains intact and unaltered during transit. They provide mechanisms to detect any tampering or modifications to the transmitted data, enhancing data integrity and reliability.
- Access to Restricted Content. VPN protocols allow users to bypass geo-restrictions and access content and services that might be limited to specific regions. This is particularly useful for streaming, accessing websites, or using online services that are not available in certain locations.
- Versatility (Various Use-Cases). Different VPN protocols offer varying trade-offs between security, speed, and compatibility. Users can choose protocols that best suit their specific needs, whether it’s prioritizing speed for activities like streaming or focusing on robust security for sensitive transactions.
- Adaptability. As technology evolves and new security threats emerge, VPN protocols can be updated and adapted to address these challenges. This ensures that VPNs remain effective tools for maintaining online security and privacy.
It is safe to say that VPN protocols are the building blocks that define how VPNs operate and deliver on their promises of security, privacy, and accessibility. Choosing the right protocol can tailor the VPN experience to individual requirements while ensuring that data remains confidential and protected throughout its journey across the digital landscape.
Types of VPN Protocols
There’s a diverse array of VPN protocols, each designed with specific attributes to cater to various needs and preferences. Among the notable contenders are OpenVPN, renowned for its open-source nature, flexibility, and robust security features. L2TP/IPsec, on the other hand, combines Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) for tunnel creation with IPsec for encryption, presenting a balanced blend of security and compatibility.
The IKEv2/IPsec protocol emphasizes seamless device switching and resumption of connections, making it ideal for mobile users. PPTP, an older protocol, prioritizes speed but offers comparatively weaker security, while SSTP leverages the SSL/TLS protocols for a secure connection, primarily favored by Windows users. WireGuard, a newer addition, boasts minimal code for enhanced performance and security. The choice of protocol depends on individual priorities, be it striking a balance between speed and security, optimizing for specific devices, or accommodating geographical access needs.
Most Common VPN Protocols
IPSec
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) serves as a robust VPN tunneling protocol that enhances data exchange security by enforcing both session authentication and encryption of data packets. This dual-layered approach involves embedding an encrypted message within the data packet, which is then encrypted again. To bolster its security, IPSec often collaborates with other protocols and is favored for Site-to-site VPN configurations due to its strong compatibility.
IKEv2
Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) operates as a tunneling protocol rooted in IPsec principles, forging a robustly secure conduit for VPN communication between devices. It delineates the framework for negotiating and authenticating IPsec security associations (SAs), underpinning the establishment of a safeguarded virtual private network. This amalgamation is commonly denoted as IKEv2/IPsec, encapsulating both the proficiency of IKEv2 as a key management protocol and the tunneling capabilities of IPsec for data transport.
PPTP
PPTP, an acronym for Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, has stood the test of time as one of the oldest VPN protocols still in active use. Since its inception in the era of Windows 95, PPTP has been an integral part of all Windows versions. Operating on TCP port 1723, it was initially developed by Microsoft to encapsulate the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP).
SSTP
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) has emerged as a prominent player in the realm of Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections. Originating from Microsoft, SSTP is notably more ingrained in Windows ecosystems than in Linux environments. Microsoft conceived this technology as an upgrade over the comparatively less secure PPTP or L2TP/IPSec options available on Windows systems. SSTP has naturally become a native preference for VPN connections in Windows, with its adoption contingent upon the VPN service provider’s strategy and its inherent user and administrative advantages.
L2TP
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) functions by establishing a secure tunnel between two L2TP connection points. Once this tunnel is established, an additional tunneling protocol, typically IPSec, is employed to encrypt the transmitted data. L2TP’s intricate architecture ensures a high level of data security. It is a prevalent choice for Site-to-site setups, particularly when heightened security is of paramount importance.
SSL/TLS
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are standards that encrypt HTTPS web pages, limiting user access to specific applications rather than the entire network. SSL/TLS connections, integrated into most web browsers, eliminate the need for additional software, making them ideal for remote access VPNs.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN, an open-source extension of the SSL/TLS framework, augments its encrypted tunnel with additional cryptographic algorithms for heightened security. Although esteemed for its strong security and efficiency, compatibility and setup can be inconsistent, especially for router-to-router VPN networks. OpenVPN offers User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) versions, with UDP prioritizing speed and TCP ensuring data integrity. Popular for remote access and Site-to-site VPN applications, OpenVPN remains a well-rounded choice.
SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) generates encrypted connections and permits port forwarding to remote machines via a secure channel. While it provides flexibility, SSH channels require vigilant monitoring to avoid creating a potential entry point for breaches, making it better suited for remote access scenarios.
Wireguard
Wireguard, a recent addition, offers a less intricate yet more efficient and secure tunneling protocol than IPSec and OpenVPN. Leveraging streamlined code for optimal performance and minimal error, Wireguard is increasingly adopted, including in Site-to-site connections such as NordLynx, a proprietary WireGuard implementation by NordVPN.
Hybrid VPN Protocols
A hybrid VPN protocol combines the strengths of different protocols to optimize security, speed, and compatibility. By integrating features from various protocols, a hybrid VPN protocol aims to deliver a well-rounded solution that adapts to different scenarios. This approach seeks to provide a balance between robust encryption, reliable performance, and the ability to bypass network restrictions, making it a versatile choice for users seeking a comprehensive VPN experience.
IKEv2/IPSec
The IKEv2/IPSec hybrid protocol refers to a combination of two distinct but complementary protocols: Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) and Internet Protocol Security (IPSec). IKEv2 is responsible for managing the establishment and maintenance of secure VPN connections, while IPSec handles the encryption and authentication of data transmitted over the network. This hybrid protocol offers a potent combination of rapid connection establishment, strong security through encryption, and adaptability to various network conditions, making it an effective solution for ensuring privacy and data protection in online communications.
L2TP/IPSec
The L2TP/IPSec hybrid protocol is readily available in most mobile and desktop operating systems, simplifying its implementation. This protocol offers heightened security by incorporating a double encapsulation feature, providing dual layers of protection for your data. Despite its widespread usage, the protocol is limited to utilizing UDP port 500 for connections, necessitating supplementary configurations to bypass firewalls.
However, a drawback of the L2TP/IPSec hybrid protocol is its relatively slower speeds. This is attributed to the process of converting traffic into L2TP format before encryption occurs. The double encapsulation nature of the protocol demands increased resources for transmitting data packets through tunnels, resulting in a reduction in transfer speeds compared to other options.
Proprietary VPN Protocols
A proprietary VPN protocol refers to a unique and exclusive communication protocol developed and owned by a particular company or organization. Unlike open-source protocols that are openly available and can be reviewed and modified by the broader community, proprietary protocols are typically kept under the control of their creators.
These protocols are often designed with specific features, optimizations, or security mechanisms tailored to the company’s goals or products. While proprietary protocols can offer certain advantages or innovations, they also come with potential drawbacks. Users may have limited visibility into how the protocol functions or the level of security it provides, as the inner workings might not be disclosed to the public. Compatibility with third-party software or devices could be more restricted compared to widely adopted open-source alternatives.
Here are some examples of proprietary protocols.
NordLynx
Developed by NordVPN, NordLynx is a proprietary protocol based on WireGuard. It aims to provide a balance between speed and security, leveraging WireGuard’s efficiency while adding proprietary enhancements from NordVPN.
Chameleon
Created by VyprVPN, Chameleon is a proprietary protocol designed to bypass VPN blocking and throttling. It uses OpenVPN 256-bit encryption with additional obfuscation to make VPN traffic less detectable and more resistant to interference.
Catapult Hydra
This protocol is developed by AnchorFree, the company behind Hotspot Shield VPN. Catapult Hydra is designed to provide fast and secure connections by optimizing data transport and reducing latency.
Obsolete VPN Protocols
Despite still in use, these protocols can be considered archaic.
IPSec
Engineered with the aim of establishing a safe benchmark for online security, IPsec pioneered the inception of fortified internet connections. Although not as prevalent among contemporary internet security protocols, IPsec retains a crucial function in safeguarding digital communications over the internet. In that sense, despite still in use in some specific cases, IPSec is somewhat obsolete.
PPTP
Point–to–Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), while a tunneling protocol that creates a ciphered tunnel, has become less favored due to its susceptibility to brute-force attacks. The cipher, developed in the ’90s, has proven vulnerable to modern computing power. Consequently, it is infrequently used, with more secure tunneling protocols featuring advanced encryption being the preferred alternatives.
VPN Protocols and Encryption Algorithms
Encryption algorithms play a critical role in ensuring the security and confidentiality of data transmitted through VPN protocols. Various VPN protocols utilize different encryption algorithms to achieve these goals. Here are some common encryption algorithms used in VPN protocols.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
AES is widely regarded as one of the most secure and efficient encryption algorithms. It comes in different key lengths, such as AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256, with the higher numbers indicating stronger encryption. AES is commonly used in protocols like OpenVPN, IPsec, and IKEv2.
3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard)
Although considered somewhat outdated, 3DES is still used in some older VPN implementations. It applies the DES algorithm three times in sequence to enhance security.
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
RSA is an asymmetric encryption algorithm used for key exchange and digital signatures. It’s often used in combination with other encryption algorithms for securing the initial key exchange in VPN protocols.
Diffie-Hellman (DH)
Diffie-Hellman is a key exchange algorithm used to securely negotiate secret keys between two parties. It’s frequently combined with other encryption algorithms like AES or 3DES.
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
ECC is gaining popularity due to its strong security and efficiency. It offers equivalent security to traditional encryption algorithms like RSA with shorter key lengths, making it suitable for resource-constrained devices.
Camellia
Camellia is a symmetric encryption algorithm that is often used alongside AES in VPN protocols. It is well-regarded for its security and speed.
ChaCha20
ChaCha20 is a relatively new symmetric encryption algorithm known for its speed and resistance to some types of attacks. It’s often used in conjunction with Poly1305 for message authentication.
Poly1305
While not an encryption algorithm by itself, Poly1305 is used for message authentication in combination with encryption algorithms like ChaCha20.
Blowfish
Although less common nowadays, Blowfish was one of the earlier encryption algorithms used in VPN protocols. It has been succeeded by more secure options like AES.
The choice of encryption algorithm depends on a balance between security, performance, and compatibility. Modern VPN protocols often support multiple encryption algorithms, allowing users to select the one that best aligns with their needs and priorities.
Difference Between VPN Encryption and VPN Protocols
These are two distinct but interrelated components that work together to provide secure and private communication over a Virtual Private Network.
VPN encryption refers to the process of transforming plain text data into a secure and unreadable format (cipher text) during transmission. Encryption ensures that even if intercepted by unauthorized parties, the data remains unintelligible without the appropriate decryption key. Strong encryption is essential for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of information exchanged between a user’s device and the VPN server. Encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), are used to perform this encryption. The choice of encryption algorithm and key length impacts the level of security.
A VPN protocol, on the other hand, defines the rules, procedures, and standards that govern how data is encapsulated, transmitted, and decrypted within the VPN. VPN protocols determine how the secure tunnel between the user’s device and the VPN server is established and maintained. They also specify the methods of authentication, key exchange, and data encapsulation. Different VPN protocols have varying levels of security, speed, and compatibility, making them suitable for different use cases.
VPN encryption focuses on the process of making data indecipherable to unauthorized parties during transmission, while a VPN protocol outlines the set of rules and procedures for establishing and managing secure communication channels between devices. Both components are integral to the overall security and functionality of a VPN, working together to ensure that data remains confidential, secure, and protected as it travels across potentially insecure networks.
How to Choose a VPN Protocol: Use-Cases
Selecting the right VPN protocol in 2023 is a pivotal decision that significantly impacts your online experience. Each VPN protocol comes with its own set of attributes, strengths, and trade-offs, making it essential to align your choice with your specific priorities. For those emphasizing top-tier security, protocols like OpenVPN or IKEv2/IPsec offer robust encryption and authentication mechanisms. If speed is paramount, protocols like WireGuard or PPTP might be more suitable due to their optimized data transmission.
Compatibility is also crucial, and you should take into consideration that your chosen protocol is supported by your devices and operating systems. In a nutshell, keep in mind your intended use case, whether it’s remote access, bypassing geo-restrictions, or safeguarding sensitive transactions. By evaluating factors such as security, speed, compatibility, and use cases, you can make an informed decision and select a VPN protocol that seamlessly aligns with your online protection requirements and preferences.
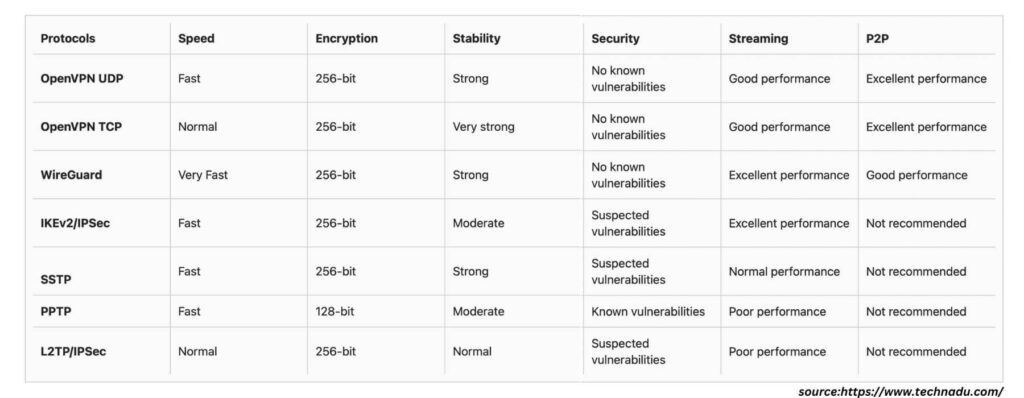
Speed
WireGuard earns its distinction as the speed champion among VPN protocols, due to its streamlined code and swift encryption techniques. While IKEv2/IPsec boasts commendable velocity, it does so by compromising on security, rendering it an unadvisable choice when pitted against WireGuard.
WireGuard’s supremacy in velocity finds its roots in its exclusive use of UDP, circumventing OpenVPN’s TCP validations. Moreover, its exceptionally efficient codebase boasts a mere 4,000 lines, simplifying and expediting security audits.
Security
Ranked as the pinnacle of VPN security, OpenVPN owes its status to an extensive community of developers who consistently subject its code to vulnerability assessments. Fortified by robust military-grade AES 256-bit encryption, OpenVPN holds the edge over WireGuard, which employs the more recent ChaCha20 encryption standard.
OpenVPN’s formidable security is attributed to its distinctive security protocol, forming point-to-point connections and enabling key exchanges supported by SSL/TLS. Its resilience is further demonstrated by its adaptability, as it traverses both TCP and UDP, thwarting attempts at blockage. Keep in mind, though, that due to its intricate nature, configuring OpenVPN manually requires a degree of technical acumen.
Stability
IKEv2/IPsec stands out for its exceptional stability, facilitating seamless network transitions devoid of connection losses or privacy compromises. However, this convenience comes at the cost of security, as there are concerns about potential vulnerabilities embedded within its code.
The allure of IKEv2/IPsec lies in its broad compatibility, extending its support to a diverse spectrum of devices and platforms, spanning routers, Linux, iOS, macOS, Android, and Windows. Remarkably, this protocol achieves unparalleled performance on macOS systems. This level of stability has led several VPN providers to adopt IKEv2/IPsec as their default protocol within their applications.
Gaming
When it comes to gaming, WireGuard emerges as the undisputed champion of VPN protocols, owing to its speed capabilities. However, its effectiveness in circumventing firewalls is somewhat limited. If you encounter persistent connection interruptions, exploring SSTP might be worthwhile, especially if stringent privacy and security considerations aren’t paramount.
WireGuard’s standout advantage in gaming lies in its potential to significantly lower latency. Its architecture is engineered to optimize packet routes, thereby mitigating packet loss and tackling irksome ping-related problems effectively.
Geo-Restricted Content / Streaming
When it comes to streaming, OpenVPN is considered the optimal VPN protocol, excelling in effortlessly circumventing geo-restrictions and firewalls. Streaming platforms like HBO Max, Netflix, and Hulu frequently mount barriers against VPN access, necessitating a protocol such as OpenVPN, capable of consistently evading VPN detection mechanisms.
OpenVPN boasts further advantages, including its fleet-footed servers and minimal degradation in connection speeds. With an Internet connection clocking in at a minimum of 4 Mbps, OpenVPN ensures a seamless experience streaming full HD videos, effectively circumventing buffering concerns.
Torrenting
For torrenting, OpenVPN takes the lead as the best VPN protocol, primarily owing to its robust security features. In the realm of torrent downloads, safeguarding privacy and shielding one’s identity reign supreme, with speed taking a secondary role.
WireGuard can also be considered a viable option. However, it employs the more recent ChaCha20 encryption, a choice that hasn’t undergone as extensive testing as OpenVPN’s AES 256-bit encryption. While WireGuard generally garners confidence in terms of safety, some privacy-conscious users willing to avoid encountering any potential copyright infringement predicaments, might find this encryption aspect disconcerting.
Mobile
IKEv2 is often favored for mobile devices due to its ability to quickly reconnect after network changes or device sleep. It’s efficient for maintaining a stable connection, making it ideal for users on the move. It’s also available on most mobile platforms.
WireGuard, on the other hand, is known for its speed and efficiency, which can be advantageous for mobile devices with potentially less powerful hardware or varying network conditions. It’s designed to be lightweight and is gaining popularity for mobile VPN applications.
OpenVPN is a versatile and widely supported protocol that can be a solid choice for mobile devices. It’s known for its strong security features and is available on various platforms.
Lastly, L2TP/IPsec is a secure option that’s built into many mobile devices. While it may not offer the same level of speed as some other protocols, it can be a good choice if security is a top priority.
Conclusion
Whether prioritizing ironclad encryption, lightning-fast speeds, or seamless access to geo-restricted content, each protocol offers a distinct blend of strengths. Yet, united in their pursuit of secure communication, these protocols empower us to traverse the virtual landscape with confidence, ensuring that our data remains shielded, and our identities protected.
Resources
- Types of VPNs & Protocols (https://nordlayer.com/)
- VPN protocols explained (https://cybernews.com/)
- The best VPN protocols (https://nordvpn.com/blog/)
- VPN Protocols Explained & Compared (https://www.technadu.com/)